Microsporidia
References
Canning, E. U. 1998. Evolutionary relationships of Microsporidia. Pages 77-90 in Evolutionary Relationships among Protozoa (G. H. Coombs, K. Vickerman, M. A. Sleigh, and A. Warren, eds.) Chapman & Hall, London.
Fast, N. M., J. M. Logsdon, and W. F. Doolittle. 1999. Phylogenetic analysis of the TATA box binding protein (TBP) gene from Nosema locustae: evidence for a microsporidia-fungi relationship and spliceosomal intron loss. Molecular Biology and Evolution 16:1415-1419.
Fischer, W. M. and J. D. Palmer. 2005. Evidence from small-subunit ribosomal RNA sequences for a fungal origin of Microsporidia. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 36:606-622.
Germot, A., H. Philippe, and H. Le Guyader. 1997. Evidence for loss of mitochondria in Microsporidia from a mitochondrial-type HSP70 in Nosema locustae. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 87:159-168.
Hirt, R. P., B. Healy, C. R. Vossbrinck, E. U. Canning, and T. M. Embley. 1997. A mitochondrial Hsp70 orthologue in Vairimorpha necatrix: Molecular evidence that microsporidia once contained mitochondria. Current Biology 7:995-998.
Hirt, R. P., J. M. Logsdon, Jr., B. Healy, M. W. Dorey, W. F. Doolittle, and T. M. Embley. 1999. Microsporidia are related to fungi: evidence from the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II and other proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 96:580-585.
Keeling, P. J., M. A. Luker, and J. D. Palmer. 2000. Evidence from beta-tubulin phylogeny that microsporidia evolved from within the fungi. Molecular Biology and Evolution 17:23-31.
Keeling, P. J. and G. I. McFadden. 1998. Origins of microsporidia. Trends Microbiol. 6:19-23.
Li, J., S. K. Katiyar, A. Hamelin, G. S. Visvesvara, and T. D. Edlind. 1996. Tubulin genes from AIDS-associated microsporidia and implications for phylogeny and benzimidazole sensitivity. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 78:289-295.
Lom, J. and F. Nilsen. 2003. Fish microsporidia: fine structural diversity and phylogeny. International Journal for Parasitology 33:107-127.
Sprague, V., J. J. Becnel, and E. I. Hazard. 1992. Taxonomy of phylum Microspora. Critical Reviews in Microbiology 18(5-6):285-395.
Van de Peer, Y., A. Ben Ali, and A. Meyer. 2000. Microsporidia: accumulating molecular evidence that a group of amitochondriate and suspectedly primitive eukaryotes are just curious fungi. Gene 246:1-8.
Vossbrinck, C. R., T. G. Andreadis, J. Vavra, and J. J. Becnel. 2004. Molecular phylogeny and evolution of mosquito parasitic microsporidia (Microsporidia : Amblyosporidae). Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 51(1):88-95.
Vossbrinck, C. R. and B. A. Debrunner-Vossbrinck. 2005. Molecular phylogeny of Microsporidia: ecological, ultrastructural and taxonomic considerations. Folio Parasitologica 52:131-142.
Title Illustrations

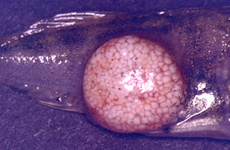
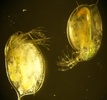
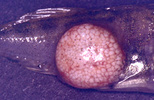
| Scientific Name | Glugea anomala |
|---|---|
| Comments | host cell of the stickleback Gasterosteus (Pisces:Teleostei) filled with microsporidian spores is hypertrophied to a macroscopic cyst (xenoma). |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | spores |
| Copyright | © 2004 Ronny Larsson |
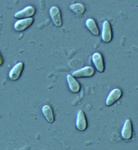
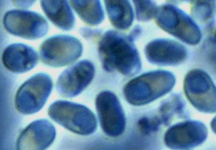
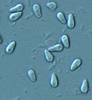
| Scientific Name | Glugea anomala |
|---|---|
| Comments | fresh spores isolated from the tissue cyst of the stickleback. Many fish microsporidia have a very large vacuole in their spores. |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | spores |
| Copyright | © 2004 Ronny Larsson |
About This Page
Page copyright © 2012
All Rights Reserved.
- First online 09 January 2008
- Content changed 09 January 2008
Citing this page:
Tree of Life Web Project. 2008. Microsporidia. Version 09 January 2008 (temporary). http://tolweb.org/Microsporidia/2378/2008.01.09 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/






 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site